Exploring Major Differences Between the WNBA and NBA
The Women's National Basketball Association (WNBA) and the National Basketball Association (NBA) share fundamental parts of the basketball experience. However, a closer look reveals a range of differences-from player salaries to game structure, and even the ball specifications. This in-depth comparison highlights 14 significant distinctions between these two professional basketball leagues.
Salary Disparities: NBA vs. WNBA Earnings
When examining earnings in professional basketball, the divide is stark. During the 2023-24 season, NBA teams operated under a $135 million salary cap, with the average player's annual salary exceeding $10 million. Rookies started at $1.1 million, while seasoned veterans earned at least $1.86 million annually. The financial scale in the WNBA is dramatically different: the league’s salary cap stood at just $1.46 million per team, and the average salary was $116,580. The minimum salary for WNBA players was $64,154, with players entering their third year earning no less than $76,535.
Stephen Curry led the NBA in salary, earning $51.9 million per season, with nine other stars making over $45 million. By contrast, Jackie Young of the Las Vegas Aces topped the WNBA at $252,450. Fewer than two dozen WNBA athletes earned $200,000 or more.

Rookie star Caitlin Clark, who made history in the NCAA, was drafted first by the Indiana Fever but will earn only $76,535 in her freshman WNBA season. In the NBA, top draft pick Victor Wembanyama started much higher, with $12.16 million in his debut season.
Three-Point Lines: Distance Makes a Difference
While both leagues share the concept of a three-point line, its placement varies. The NBA’s arc is 22 feet from the rim in the corners, extending to 23.75 feet at the top of the key. The WNBA’s line is slightly closer-corner shots are 21.75 feet away, and the arc widens to 22 feet at the top.
Basketball Specifications: Size and Weight
Another physical distinction lies in the ball itself. The WNBA uses a size 6 ball, measuring 28.5 inches in diameter and weighing 20 ounces, featuring a distinctive white and orange color. The NBA’s size 7 ball is slightly larger at 29.5 inches and 22 ounces, traditionally brown or dark orange and monochromatic.
Revenue Generation: Financial Scale of Each League
In terms of league revenue, the NBA towers above the WNBA. The NBA generated approximately $10.58 billion in the 2023 season, while the WNBA recorded $200 million. Income streams for both include television rights, sponsorships, merchandising, and ticket sales, but the NBA’s TV rights alone approached $2.7 billion annually, with owners and players dividing these funds equally.
Conversely, the WNBA secured roughly $60 million from broadcasting deals, and WNBA players receive only 10% of total league revenue, while NBA athletes take home 50%.
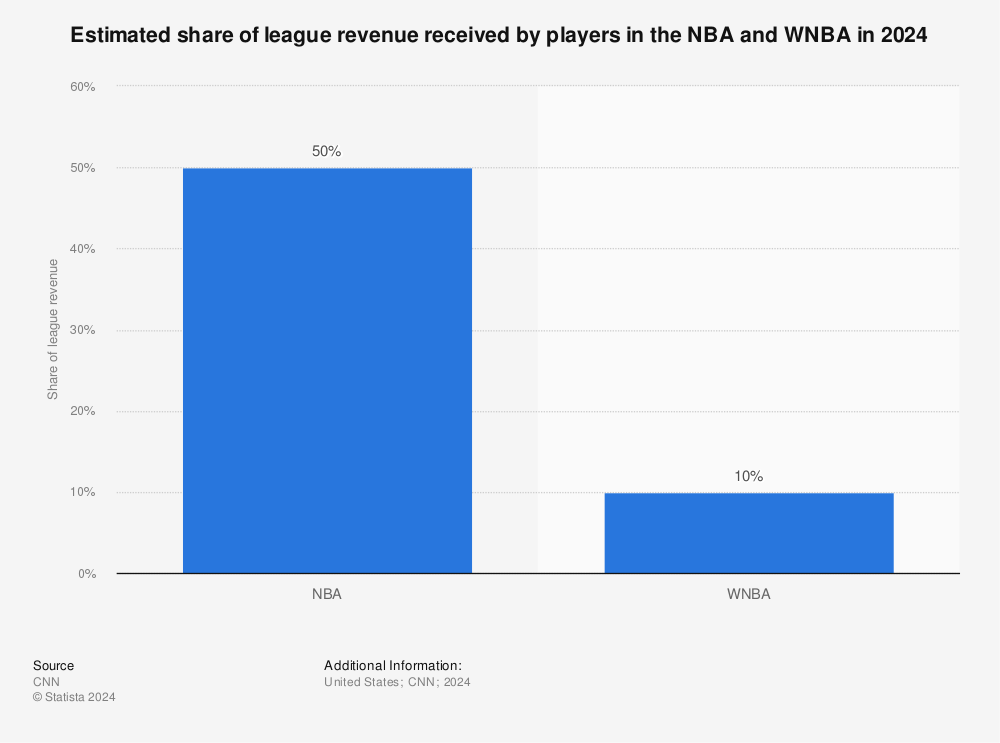
Several factors shape these financial outcomes:
- The NBA is comprised of 30 teams, while the WNBA currently has 12, expanding to 14 by 2026 with new franchises in San Francisco and Toronto.
- NBA teams compete in 82 games a season; WNBA clubs play 40.
- Ticket prices diverge as well: NBA tickets averaged $94, while WNBA tickets were typically $47, though high-profile matchups, especially involving Caitlin Clark, have pushed prices up to $108 for some away games.
Court Size: Where They’re the Same
Despite other differences, both leagues compete on regulation-size courts-50 feet wide by 94 feet long (15.24 by 28.65 meters).
Television Viewership: Trends and Record Ratings
Interest and audience numbers vary widely. The 2023 WNBA Finals, featuring the Las Vegas Aces and the New York Liberty, attracted an average of 728,000 viewers per game-a 36% rise over the prior year. The 2023 and 2024 WNBA Drafts both set new benchmarks, with the latter drawing 2.4 million viewers, up 307% year-on-year.
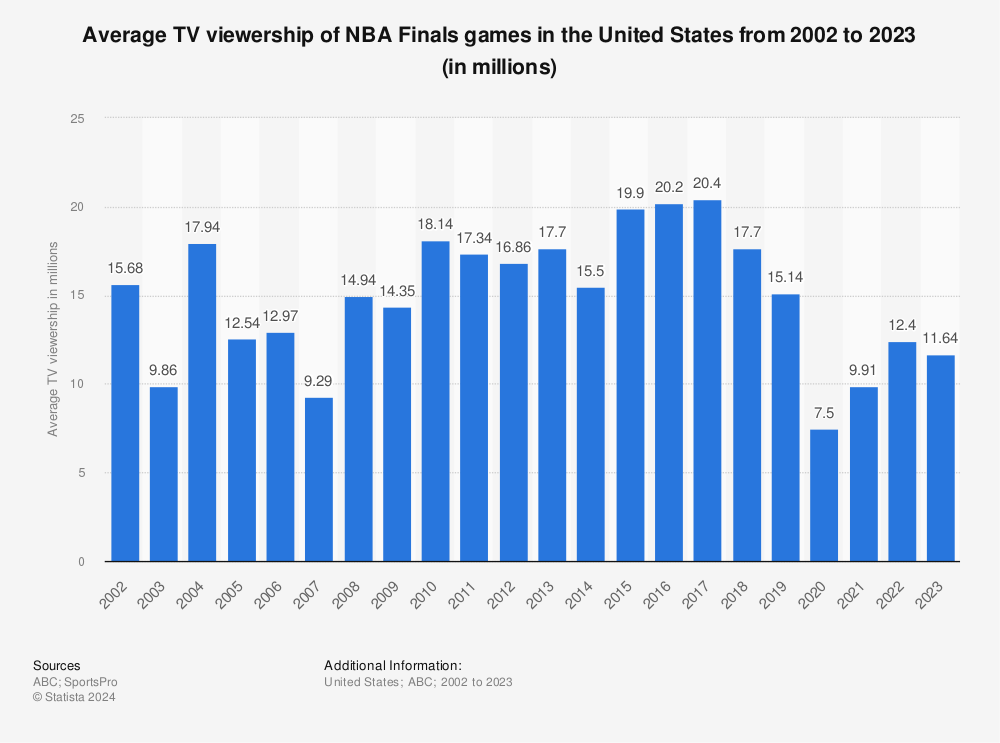
In comparison, the NBA averaged 1.2 million viewers per game during the 2023-24 regular season. The NBA Finals, featuring the Denver Nuggets and Miami Heat, saw an audience of 11.64 million-the largest in five years.
Fan Attendance: Crowds in the Arena
The WNBA saw a resurgence in 2023, boosting its season to 40 games and selling over 1.58 million tickets, returning to its highest attendance in 13 years. The average crowd reached 6,615 fans per game, with the Las Vegas Aces leading with over 9,500 fans per home game.
Meanwhile, the NBA broke its own attendance records, with over 22.5 million fans attending the 2023-24 season and an average of 18,324 fans per game. The Chicago Bulls led the league with 845,620 tickets sold.
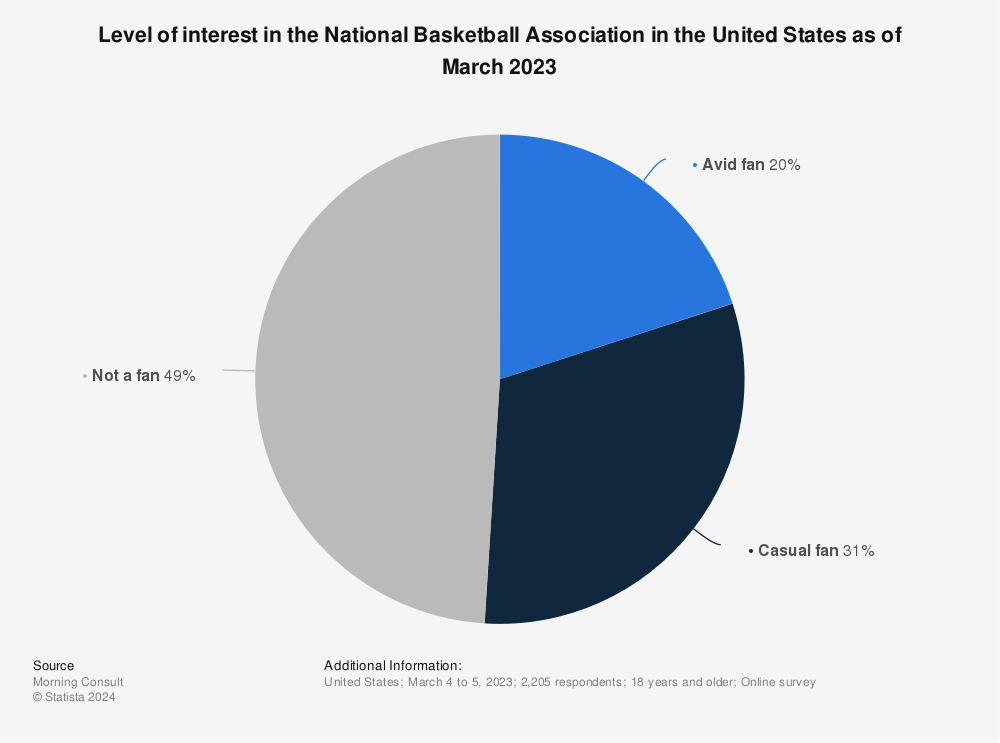
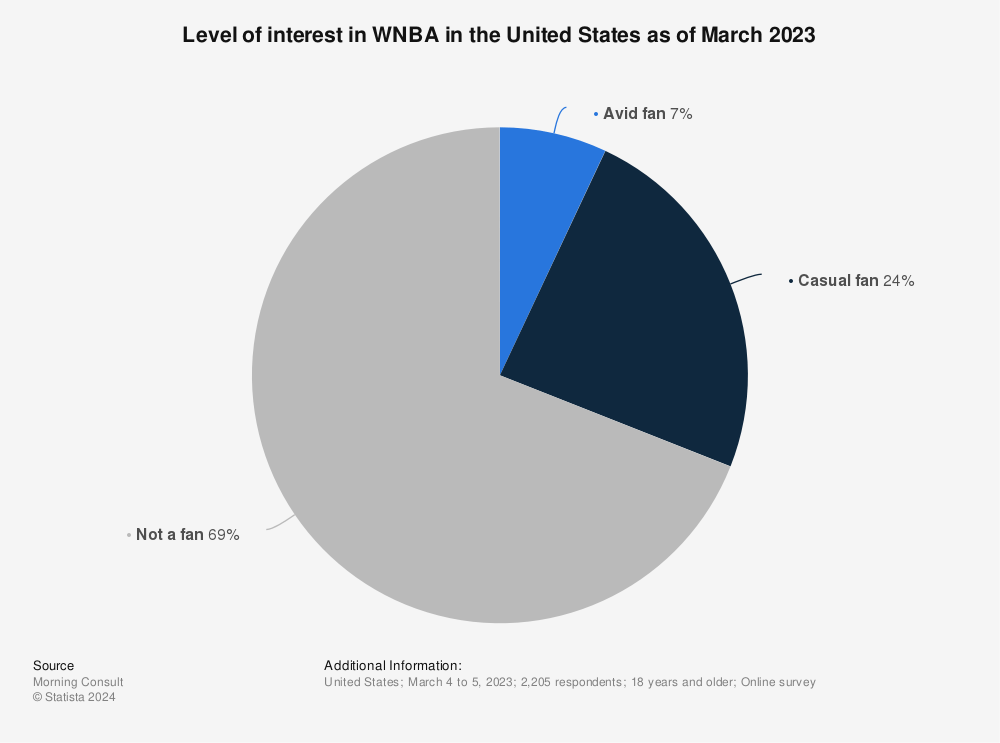
A 2023 survey underscored the gap, showing that 50% of respondents were interested in the NBA compared to approximately 30% for the WNBA.
Hoop and Backboard Dimensions: A Shared Standard
Both leagues use identical basketball equipment: the rim stands at 10 feet tall and is 18 inches in diameter, mounted to the same size backboard.
Elite Players vs. Bench Athletes: Comparing Standouts and Roster Depth
In the WNBA, A’ja Wilson has dominated, leading the Las Vegas Aces to consecutive championships and capturing the Finals MVP title in 2023, with averages such as 23.8 points, 11.8 rebounds, and 2.3 blocks per game in the postseason.

For NBA comparison, players who see limited minutes or serve mainly as depth-like Dalen Terry of the Chicago Bulls or Buddy Boeheim of the Detroit Pistons-typically average low single digits in major stats. Hypothetically, these NBA bench players have significant size and athletic advantages over WNBA stars, making interleague play highly speculative.
Top Teams and Struggling Squads: Success at Both Extremes
The Las Vegas Aces are currently the benchmark in the WNBA, winning back-to-back championships and setting a record 34-6 season. On the other end, the Detroit Pistons have struggled, notching only 14 wins in the 2023-24 NBA season and enduring a historic 28-game losing streak.
A hypothetical matchup would still lean heavily to the NBA team, given notable height and depth differences.
Dunks: Rarity Versus Routine
Slam dunks are iconic in the NBA but remain rare in the WNBA, with only eight women ever achieving an in-game dunk. Lisa Leslie recorded the first in 2002, with Brittney Griner and Jonquel Jones currently the only active women with dunks to their names. In contrast, NBA players, regardless of height-like the 5-foot-7 Spud Webb-regularly wow crowds with their leaping ability.

Championship Parades: Celebration Scale
Victory parades in the NBA can be massive events, sometimes drawing over a million fans, as witnessed when Cleveland celebrated its 2016 championship. WNBA parades are more modest, although cities like Las Vegas have enthusiastically celebrated their Aces’ titles with festivities along the vibrant Strip.
Game Structure and Rules: Contrasts in Competition
Key differences in regulations between the leagues include:
- The NBA features four quarters of 12 minutes each (totaling 48 minutes per game), while the WNBA uses four 10-minute quarters (40 minutes).
- Both use the same court and rim dimensions, but the WNBA three-point line is closer.
- Shot clocks differ: 24 seconds in the NBA, 30 in the WNBA.
- NBA rosters can have 15 players plus two additional temporary contracts; the WNBA allows only 12.
- Draft eligibility also varies: WNBA athletes must be college seniors or at least 22 years old, while the NBA requires players to be at least 19 and one year removed from high school graduation.
Free Throw Accuracy: Shooting Success Rates
Free throw shooting is an area where the WNBA often holds a slight edge. The league has averaged above 79% in the past decade and finished at 80% in 2023, peaking at 80.8% in 2021. Meanwhile, the NBA averaged 77.8% over recent seasons, with a record 78.4% success rate just last season.
Conclusion: Unique and Evolving Leagues
While the WNBA and NBA play by the same core rules, layered distinctions exist in their financials, viewing audiences, gameplay structure, and culture. Both leagues continue to shape their identities, foster passionate fan bases, and push for new milestones-ensuring each offers its own distinct chapter in the world of professional basketball.













